- maison
- >
- Nouvelles
- >
- die casting manufacturing
- >
- Can magnesium alloy die castings be popular in automotive lightweighting?
Can magnesium alloy die castings be popular in automotive lightweighting?
The lightweight of the car is to “slim down” the car, and on the basis of ensuring stable and improved performance, energy-saving design of various components and continuous optimization of the model. The experiment proves that if the weight of the whole vehicle is reduced by 10%, the fuel efficiency can be increased by 6%~8%; the weight of the car is reduced by 1%, the fuel consumption can be reduced by 0.7%; for every 100 kilograms of the car's whole weight, the fuel consumption per 100 kilometers can be reduced by 0.3~0.6. Rise.
Lightweight trend of cars
Tsinghua University Professor Ouyang Ming, on behalf of the Energy Conservation and New Energy Vehicle Development Strategy Advisory Committee, has published the contents of the energy-saving and new-energy vehicle technology roadmap. The light-weight technology development ideas proposed in the roadmap are mainly implemented in three stages. Lose weight year by year.
The first phase is from 2016 to 2020, achieving a 10% reduction in vehicle weight compared to 2015. Focus on the development of ultra-high-strength steel and advanced high-strength steel technology, including material performance development, lightweight design methods, forming technology, welding process and test evaluation methods, etc., to achieve high-strength steel in automotive applications, the proportion of more than 50%, the development of aluminum alloy Research on sheet metal stamping technology and practice in the body, study the connection technology of different materials.
The second phase is from 2021 to 2025, achieving a 20% reduction in vehicle weight compared to 2015. With the third-generation automotive steel and aluminum alloy technology as the main line, it realizes the mixing of various materials such as steel and aluminum, and the wide-area application of the all-aluminum body to realize the mass production and industrial application of aluminum alloy cover parts and aluminum alloy parts. Increase the development of production technology for magnesium alloy and carbon fiber composite parts, increase the application ratio of magnesium alloy and carbon fiber parts, and the aluminum volume for bicycles reaches 350kg.
The third phase is from 2026 to 2030, achieving a 35% reduction in vehicle weight compared to 2015. Focus on the development of magnesium alloy and carbon fiber composite technology, solve the problem of recycling of magnesium alloy and composite materials, realize the wide-ranging application of carbon fiber composite material mixing body and carbon fiber parts, and break through complex part forming technology and heterogeneous parts connection technology. The magnesium alloy for bicycles reaches 45kg, and the carbon fiber usage accounts for 5% of the vehicle weight.
According to statistics, in 2016, the amount of magnesium alloy with one car produced in China was only 7.3kg, which is still far from the target of 45kg for magnesium alloy with one car in 2030. Magnesium alloy has a broad market for lightweight applications in the future and has unlimited potential.
Magnesium alloy properties and advantages
Low density
The density of die-cast magnesium alloy is only 2/3 of aluminum alloy, 1/4 of steel, specific strength and specific stiffness are better than steel and aluminum alloy, much higher than engineering plastics, so die-cast magnesium alloy is an excellent in many A lightweight structural material that can compete with the above materials in the field of application.
Good vibration absorption
It is beneficial for vibration reduction and noise reduction. For example, at a stress level of 35 MPa, the attenuation coefficient of magnesium alloy AZ91D is 25%, and that of aluminum alloy A380 is only 1%. At 100MP stress levels, magnesium alloys AZ91D, AM60, and AS41 are 53%, 72%, and 70%, respectively, and aluminum alloy A380 is only 4%.
High dimensional stability
The dimensional instability of magnesium alloy die castings due to changes in ambient temperature and time is reduced.
High thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of magnesium alloy (60-70W/m-1 K-1) is second only to aluminum alloy (about 100-70W m-1 K-1), so the thermal diffusivity is good.
Non-magnetic, can be used for electromagnetic shielding.
Good wear resistance
Magnesium alloy also has a good damping coefficient. The damping capacity is greater than that of aluminum alloy and cast iron. It can be used for housing to reduce noise. It can be used for seats and wheels to reduce vibration and improve the safety and comfort of the car. Magnesium alloy is light in weight, strong in shock absorption performance, good in casting performance, high in automatic production capacity and die life, and dimensionally stable. As the lightest engineering material, magnesium alloy is not only the most suitable material for casting auto parts, but also the most effective car light. Quantify materials.
Status of magnesium alloy automotive die casting industry
The lightweight development of automobiles has increased the demand for light alloy castings such as magnesium and aluminum. Since 1990, magnesium for automobiles has been growing at an average annual growth rate of 20%. Magnesium alloys have become an important field in the development of automotive materials technology. Die-casting magnesium alloy materials are particularly suitable for recycling economy, energy saving, low carbon and clean production requirements due to their recyclability and low chipless process. They are dominant in the development of automobiles to lightweight. Major auto parts manufacturers actively seized the opportunity of development and invested in the production and development of magnesium alloy automotive die castings. According to the "China Magnesium Alloy Automotive Die Casting Industry Analysis Report" data, in 2015, China's magnesium alloy automotive die casting industry demand reached 149,000 tons, an increase of 23.12%. At present, domestic and foreign auto companies are working on the body (about 30%), engine (about 18%), transmission system (about 15%), walking system (about 16%), and wheels (about 10%). 5%) Magnesium alloying of steel or aluminum parts.
In view of the use of magnesium alloys per vehicle produced in China, the market capacity of China's magnesium alloy automotive die-casting industry will reach 229,000 tons in 2017, and the market capacity will reach 660,000 tons by 2022, with an average annual compound growth rate of 23.5%.
The global use of magnesium for bicycles is low, and the demand for expansion of magnesium alloys for automobiles is strong. Lightweight materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum alloy, and engineering plastics have been widely used in various aspects of automobile and auto parts manufacturing.
Magnesium alloys have not been widely promoted and used for various reasons. Magnesium alloys are mainly used in instrument panels. Bracket, steering bracket, hood, steering wheel, seat bracket, interior door panel, transmission housing, etc. At present, each car in North America uses 3.8kg of magnesium alloy, 9.3kg in Japan, and 14kg of magnesium alloy for each car on European PASSAT and Audi A4, while the average consumption of domestically produced cars is only 1.5kg per vehicle.
Application of magnesium alloy in automobile lightweighting

Car interior structure
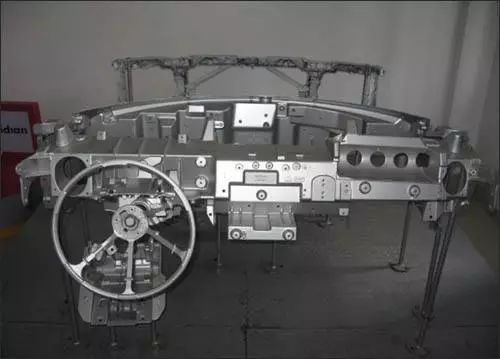
Although magnesium alloys have poor corrosion resistance, corrosion protection is not a major consideration for automotive interior construction. Therefore, magnesium alloys have been widely used in automotive interior construction, especially in instrument panels and steering structures. It is reported that the first magnesium alloy instrument panel pillar was die-casted by General Motors in 1961, saving 4 kg of material compared to the same parts produced by zinc alloy die-casting. Over the past decade or so, the use of magnesium alloy die-casting instrument tray pillars has made great progress.
The application of magnesium alloy in the seat began in Germany in the 1990s, mainly in the SL Roadster using a three-point seat belt structure made of magnesium die-casting. Similar to the application of magnesium alloy on the instrument panel, in recent years, the design and manufacture of seats made of magnesium alloy has undergone a significant improvement process. The seat structure with magnesium alloy can now be as thin as 2mm, which greatly reduces the weight. Although other materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum, and composite materials are also used, experts predict that magnesium alloys will become a major material for lightweight and cost-effective automotive seat components in the future.
Body
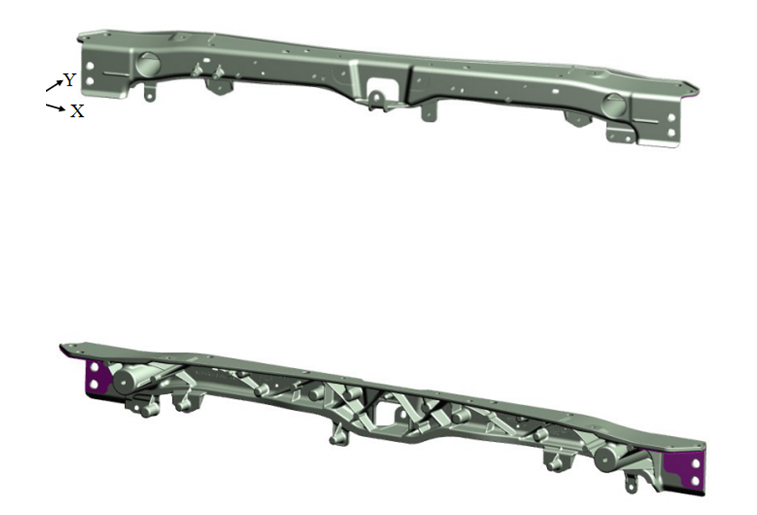
Magnesium alloys are limited in body applications, but they are also used in OEMs. When the C-5 Corvette was introduced in 1997, the entire magnesium alloy die-cast roof frame was used. In addition, the magnesium alloy was also applied to the retractable hardtop convertible roof and top frame of the Cadillac XLR Convertible. Ford F The -150 truck and SUV also use a coated magnesium casting as a heat sink bracket. In Europe, Volkswagen and Mercedes-Benz have taken the lead in the application of thin-walled magnesium alloy castings in body panels.
Chassis
Currently, cast or wrought magnesium alloy wheels have been used in many high-priced racing cars or high-performance sports cars. However, the relatively high cost and potential corrosion problems of magnesium alloy wheels prevent their use in high volume production vehicles.
In the future, the production of lightweight, low-cost magnesium alloy chassis components, such as hubs, engine suspensions, and control arms, will rely heavily on the magnesium alloy casting process, and have been developed on aluminum alloy wheels and chassis components. The casting process can be successfully applied to magnesium alloys after modification. In addition, the development of low-cost, corrosion-resistant layers and new magnesium alloys with fatigue and high impact strength will accelerate the use of magnesium alloys on the chassis.
Powertrain
Most of the castings of the powertrain, such as the engine block, cylinder head, transmission case, oil pan, etc., are made of aluminum alloy. At present, pickup trucks and SUVs produced in North America have been magnesium alloy transmissions, and Volkswagen and Audi's magnesium alloy manual transmissions are also mass-produced in Europe and China.
At present, effective progress has been made through dynamometer tests on magnesium-enhanced engine prototypes, which means that more magnesium alloys will be used in power systems in the future.
Main challenges in the promotion and application of magnesium alloys.
Poor corrosion resistance, high cost and high scrap rate are the popular barriers to magnesium alloys.
Magnesium alloys do not have the problems of high cost of die casting, high scrap rate, and hidden dangers of safe production. Du Fangci, an adviser to the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, said that magnesium is a very active element and its corrosion resistance is very poor. China's technical ability in the corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy parts is worse. In addition, magnesium is prone to combustion and explosion during processing, and there are safety production problems. Production sites require strict management to ensure safe production.
With the acceleration of urbanization, energy is becoming more and more scarce, and environmental pollution is becoming more and more serious. Energy conservation and emission reduction have become important events concerning the national economy and people's livelihood. Both traditional cars and emerging new energy vehicles pay great attention to lightweight design of the body to achieve energy saving and environmental protection.
Magnesium alloys for automobiles are booming, and the magnesium alloy die-casting process is becoming more and more mature, and the application range is expanding. Large-scale magnesium alloy die-casting auto parts will promote the process of lightweight vehicles.