- maison
- >
- Nouvelles
- >
- fabrication de moulage sous pression
- >
- Les moulages sous pression en alliage de magnésium peuvent-ils être populaires dans l’allègement automobile ?
Les moulages sous pression en alliage de magnésium peuvent-ils être populaires dans l’allègement automobile ?
L'utilisation de l'alliage de magnésium pour les sièges a débuté en Allemagne dans les années 1990, principalement sur le SL Roadster, équipé d'une ceinture de sécurité trois points moulée sous pression en magnésium. À l'instar de l'utilisation de l'alliage de magnésium pour le tableau de bord, la conception et la fabrication des sièges en alliage de magnésium ont connu ces dernières années d'importantes améliorations. La structure des sièges en alliage de magnésium peut désormais atteindre 2 mm d'épaisseur, ce qui réduit considérablement le poids. Bien que d'autres matériaux tels que l'acier haute résistance, l'aluminium et les matériaux composites soient également utilisés, les experts prédisent que les alliages de magnésium deviendront un matériau majeur pour la fabrication de sièges automobiles légers et économiques à l'avenir.
Les alliages de magnésium sont peu utilisés pour la carrosserie, mais ils sont également utilisés par les constructeurs. Lors du lancement de la Corvette C-5 en 1997, l'intégralité du cadre de toit moulé sous pression en alliage de magnésium a été utilisée. De plus, cet alliage a également été appliqué au toit rigide rétractable et au cadre supérieur de la Cadillac XLR Cabriolet. Le camion et le SUV Ford F-150 utilisent également un moulage en magnésium revêtu comme support de dissipateur thermique. En Europe, Volkswagen et Mercedes-Benz ont été les pionniers de l'utilisation de moulages en alliage de magnésium à parois minces pour les panneaux de carrosserie.
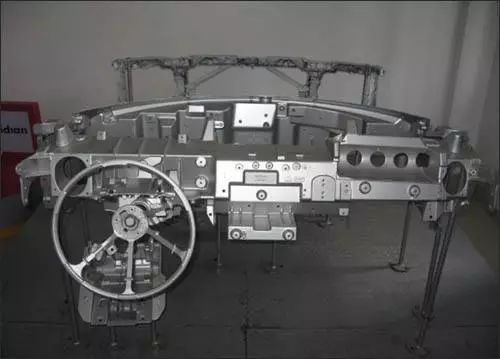
Châssis
Actuellement, les jantes en alliage de magnésium moulées ou forgées équipent de nombreuses voitures de course haut de gamme ou sportives hautes performances. Cependant, leur coût relativement élevé et les risques de corrosion qu'elles présentent empêchent leur utilisation dans les véhicules de production en grande série.
À l'avenir, la production de composants de châssis en alliage de magnésium légers et économiques, tels que les moyeux, les suspensions moteur et les bras de suspension, reposera largement sur le procédé de moulage d'alliages de magnésium. Ce procédé a été développé pour les jantes et les composants de châssis en alliage d'aluminium. Ce procédé peut être appliqué avec succès aux alliages de magnésium après modification. De plus, le développement de couches résistantes à la corrosion et de nouveaux alliages de magnésium à faible coût, offrant une résistance élevée à la fatigue et aux chocs, accélérera l'utilisation des alliages de magnésium sur les châssis.
Groupe motopropulseur
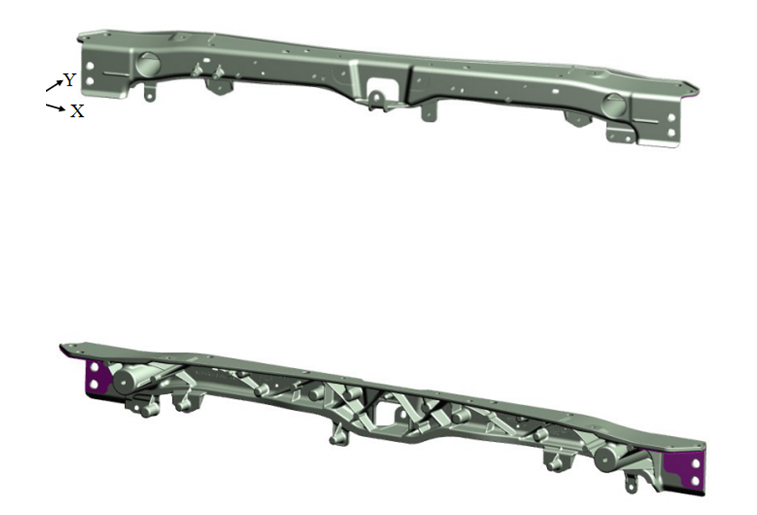
La plupart des pièces moulées du groupe motopropulseur, comme le bloc moteur, la culasse, le carter de transmission et le carter d'huile, sont en alliage d'aluminium. Actuellement, les pick-up et les SUV produits en Amérique du Nord sont équipés de transmissions en alliage de magnésium, et les transmissions manuelles en alliage de magnésium de Volkswagen et Audi sont également produites en série en Europe et en Chine.
À l’heure actuelle, des progrès efficaces ont été réalisés grâce à des tests au dynamomètre sur des prototypes de moteurs renforcés au magnésium, ce qui signifie que davantage d’alliages de magnésium seront utilisés dans les systèmes électriques à l’avenir.
Principaux défis dans la promotion et l’application des alliages de magnésium.
Une faible résistance à la corrosion, un coût élevé et un taux de rebut élevé sont les obstacles les plus courants aux alliages de magnésium.
Les alliages de magnésium ne présentent pas les inconvénients du coût élevé du moulage sous pression, du taux de rebut élevé et des dangers cachés liés à la sécurité de la production. Du Fangci, conseiller auprès de l'Association chinoise des constructeurs automobiles, a déclaré que le magnésium est un élément très actif et que sa résistance à la corrosion est très faible. Les compétences techniques de la Chine en matière de résistance à la corrosion des pièces en alliage de magnésium sont moins bonnes. De plus, le magnésium est sujet à la combustion et à l'explosion lors de la transformation, ce qui pose des problèmes de sécurité de production. Les sites de production doivent être gérés rigoureusement pour garantir la sécurité de la production.
Avec l'accélération de l'urbanisation, l'énergie se raréfie et la pollution environnementale s'aggrave. Les économies d'énergie et la réduction des émissions sont devenues des enjeux majeurs pour l'économie nationale et les moyens de subsistance de la population. Les voitures traditionnelles et les nouveaux véhicules à énergies nouvelles accordent une grande importance à la conception légère de leur carrosserie afin de réaliser des économies d'énergie et de protéger l'environnement.
Les alliages de magnésium pour l'automobile connaissent un essor considérable. Leur procédé de moulage sous pression gagne en maturité et leur champ d'application s'élargit. Le moulage sous pression à grande échelle de pièces automobiles en alliage de magnésium favorisera la fabrication de véhicules légers.
High dimensional stability
The dimensional instability of magnesium alloy die castings due to changes in ambient temperature and time is reduced.
High thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of magnesium alloy (60-70W/m-1 K-1) is second only to aluminum alloy (about 100-70W m-1 K-1), so the thermal diffusivity is good.
Non-magnetic, can be used for electromagnetic shielding.
Good wear resistance
Magnesium alloy also has a good damping coefficient. The damping capacity is greater than that of aluminum alloy and cast iron. It can be used for housing to reduce noise. It can be used for seats and wheels to reduce vibration and improve the safety and comfort of the car. Magnesium alloy is light in weight, strong in shock absorption performance, good in casting performance, high in automatic production capacity and die life, and dimensionally stable. As the lightest engineering material, magnesium alloy is not only the most suitable material for casting auto parts, but also the most effective car light. Quantify materials.
Status of magnesium alloy automotive die casting industry
The lightweight development of automobiles has increased the demand for light alloy castings such as magnesium and aluminum. Since 1990, magnesium for automobiles has been growing at an average annual growth rate of 20%. Magnesium alloys have become an important field in the development of automotive materials technology. Die-casting magnesium alloy materials are particularly suitable for recycling economy, energy saving, low carbon and clean production requirements due to their recyclability and low chipless process. They are dominant in the development of automobiles to lightweight. Major auto parts manufacturers actively seized the opportunity of development and invested in the production and development of magnesium alloy automotive die castings. According to the "China Magnesium Alloy Automotive Die Casting Industry Analysis Report" data, in 2015, China's magnesium alloy automotive die casting industry demand reached 149,000 tons, an increase of 23.12%. At present, domestic and foreign auto companies are working on the body (about 30%), engine (about 18%), transmission system (about 15%), walking system (about 16%), and wheels (about 10%). 5%) Magnesium alloying of steel or aluminum parts.
In view of the use of magnesium alloys per vehicle produced in China, the market capacity of China's magnesium alloy automotive die-casting industry will reach 229,000 tons in 2017, and the market capacity will reach 660,000 tons by 2022, with an average annual compound growth rate of 23.5%.
The global use of magnesium for bicycles is low, and the demand for expansion of magnesium alloys for automobiles is strong. Lightweight materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum alloy, and engineering plastics have been widely used in various aspects of automobile and auto parts manufacturing.
Magnesium alloys have not been widely promoted and used for various reasons. Magnesium alloys are mainly used in instrument panels. Bracket, steering bracket, hood, steering wheel, seat bracket, interior door panel, transmission housing, etc. At present, each car in North America uses 3.8kg of magnesium alloy, 9.3kg in Japan, and 14kg of magnesium alloy for each car on European PASSAT and Audi A4, while the average consumption of domestically produced cars is only 1.5kg per vehicle.
Application of magnesium alloy in automobile lightweighting

Car interior structure
Although magnesium alloys have poor corrosion resistance, corrosion protection is not a major consideration for automotive interior construction. Therefore, magnesium alloys have been widely used in automotive interior construction, especially in instrument panels and steering structures. It is reported that the first magnesium alloy instrument panel pillar was die-casted by General Motors in 1961, saving 4 kg of material compared to the same parts produced by zinc alloy die-casting. Over the past decade or so, the use of magnesium alloy die-casting instrument tray pillars has made great progress.
The application of magnesium alloy in the seat began in Germany in the 1990s, mainly in the SL Roadster using a three-point seat belt structure made of magnesium die-casting. Similar to the application of magnesium alloy on the instrument panel, in recent years, the design and manufacture of seats made of magnesium alloy has undergone a significant improvement process. The seat structure with magnesium alloy can now be as thin as 2mm, which greatly reduces the weight. Although other materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum, and composite materials are also used, experts predict that magnesium alloys will become a major material for lightweight and cost-effective automotive seat components in the future.
Body
Magnesium alloys are limited in body applications, but they are also used in OEMs. When the C-5 Corvette was introduced in 1997, the entire magnesium alloy die-cast roof frame was used. In addition, the magnesium alloy was also applied to the retractable hardtop convertible roof and top frame of the Cadillac XLR Convertible. Ford F The -150 truck and SUV also use a coated magnesium casting as a heat sink bracket. In Europe, Volkswagen and Mercedes-Benz have taken the lead in the application of thin-walled magnesium alloy castings in body panels.
Chassis
Currently, cast or wrought magnesium alloy wheels have been used in many high-priced racing cars or high-performance sports cars. However, the relatively high cost and potential corrosion problems of magnesium alloy wheels prevent their use in high volume production vehicles.
In the future, the production of lightweight, low-cost magnesium alloy chassis components, such as hubs, engine suspensions, and control arms, will rely heavily on the magnesium alloy casting process, and have been developed on aluminum alloy wheels and chassis components. The casting process can be successfully applied to magnesium alloys after modification. In addition, the development of low-cost, corrosion-resistant layers and new magnesium alloys with fatigue and high impact strength will accelerate the use of magnesium alloys on the chassis.
Powertrain
Most of the castings of the powertrain, such as the engine block, cylinder head, transmission case, oil pan, etc., are made of aluminum alloy. At present, pickup trucks and SUVs produced in North America have been magnesium alloy transmissions, and Volkswagen and Audi's magnesium alloy manual transmissions are also mass-produced in Europe and China.
At present, effective progress has been made through dynamometer tests on magnesium-enhanced engine prototypes, which means that more magnesium alloys will be used in power systems in the future.
Main challenges in the promotion and application of magnesium alloys.
Poor corrosion resistance, high cost and high scrap rate are the popular barriers to magnesium alloys.
Magnesium alloys do not have the problems of high cost of die casting, high scrap rate, and hidden dangers of safe production. Du Fangci, an adviser to the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, said that magnesium is a very active element and its corrosion resistance is very poor. China's technical ability in the corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy parts is worse. In addition, magnesium is prone to combustion and explosion during processing, and there are safety production problems. Production sites require strict management to ensure safe production.
With the acceleration of urbanization, energy is becoming more and more scarce, and environmental pollution is becoming more and more serious. Energy conservation and emission reduction have become important events concerning the national economy and people's livelihood. Both traditional cars and emerging new energy vehicles pay great attention to lightweight design of the body to achieve energy saving and environmental protection.
Magnesium alloys for automobiles are booming, and the magnesium alloy die-casting process is becoming more and more mature, and the application range is expanding. Large-scale magnesium alloy die-casting auto parts will promote the process of lightweight vehicles.